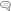SHBG, or Sex Hormone Binding Globulin, controls testosterone effect in both men and women by modulating changes in sex steroid levels. When SHBG goes up, free testosterone goes down.
I like to think of SHBG as a sponge that soaks up androgens and to some degree estrogens as well.
Since it binds so specifically and tightly to testosterone, it makes up part of the equation that equals androgen excess or androgen deficiency. Knowing how to manipulate SHBG can be a useful tool in a number of scenarios.
Role: Bind to and carry testosterone (and less strongly E2 and DHT) through the blood stream to target tissues and to the liver for modification and removal from the body. This bond is very strong. The bound testosterone is not easily removed from the SHBG and is therefore considered inactive.
Production Sites: Liver mostly, testes, brain
Production Signals: Estradiol, triiodothyronine (T3)
Down-Regulated by: Insulin
Aliases: ABP (androgen binding protein), SSBG (sex steroid binding globulin), TEBG (testosterone binding beta globulin), GBG (gonadal steroid binding globulin)
Action: Controls clearance and bioavailability of testosterone
Prescription Drugs & SHBG Levels
Some drugs such as Spironolactone alter binding of androgens to the receptor sites on SHBG, therefore leading to increased clearance of testosterone and to the rise of estrogen and SHBG. Other medications can cause a sustained increase in prolactin levels that suppress testosterone and raise SHBG. Safe to say, most if not all oral drugs have some effect on the liver and SHBG levels. Listed are some of the ones that make the most impact.
Drugs that Raise SHBG via Increasing Prolactin:
- Antipsychotics (both typical and atypical)
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, Tricyclics, MAO-Is)
- Xanax and Buspar
- H2 Antagonists (Cimetidine, Ranitidine)
- Morphine
- Some Antihypertensives
Drugs that Raise SHBG:
- Raloxifene (Evista)
- Tamoxifen
- Spironolactone
- Anticonvulsants (Phenytoin)
- Oral (but not transdermal) estradiol
- Ethinyl estradiol (oral contraceptives)
- Metformin
- Exogenous insulin in Type 2 DM
- Coffee!
Drugs that Suppress SHBG:
- Progestins
- Glucocorticoids
- Exogenous insulin in Type I DM
Genetics
- Some people have a genetic variation in their SHBG structure that slows or speeds its degradation leading to high or low levels. Current research projects are studying specific SHBG SNPs with regard to risk of Type 2 diabetes
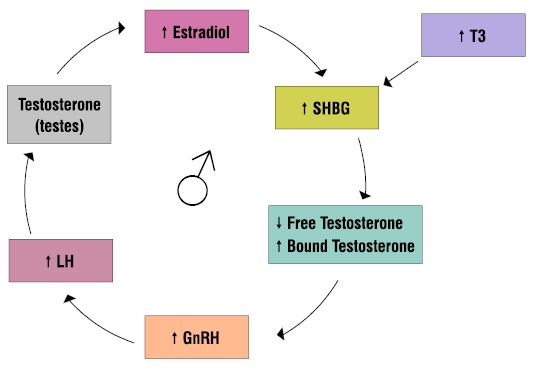
Areas of Application:
How to Influence SHBG:
Pinpoint the cause of the imbalance whenever possible and instead of trying to lower a high SHBG and raise a low SHBG, zoom out to support balance in the system. If SHBG is high or low, look deeper. Always consider the main endocrine inputs: INSULIN, ESTRADIOL, THYROID.
Accompanying Tests:
- Fasting Insulin
- HgbA1c
- Sex Steroids (E2, T, DHEA-S)
- Thyroid Panel (TSH, fT3, fT4)
- LH and FSH
- IGF-1
- Prolactin
- Liver function tests
Some Treatment Examples: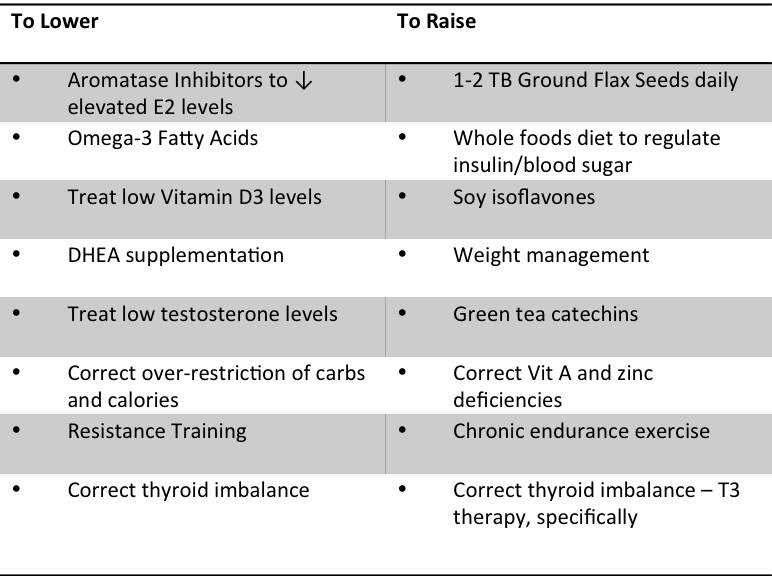
Continue the discussion: